Best Trading Analysis Tools to Buy in March 2026

Trading: Technical Analysis Masterclass: Master the financial markets
- MASTER TECHNICAL ANALYSIS FOR SMARTER TRADING DECISIONS.
- PREMIUM QUALITY MATERIAL ENHANCES READING AND LEARNING EXPERIENCE.
- UNLOCK FINANCIAL MARKET SECRETS WITH OUR EXPERT-LED GUIDE.



Gimly - Trading Chart (Set of 5) Pattern Posters, 350 GSM Candle Chart Poster, Trading Setup Kit for Trader Investor, (Size : 30 x 21 CM, Unframed)
- EYE-CATCHING GLOSS FINISH ENHANCES VISIBILITY FOR BETTER TRADING
- DURABLE 350 GSM PAPER ENSURES LONG-LASTING USE AND DISPLAY
- PERFECTLY SIZED FOR EASY FRAMING IN STOCK AND CRYPTO MARKETS



The Trader's Handbook: Winning habits and routines of successful traders



Options Trading: How to Turn Every Friday into Payday Using Weekly Options! Generate Weekly Income in ALL Markets and Sleep Worry-Free!


![The Candlestick Trading Bible [50 in 1]: Learn How to Read Price Action, Spot Profitable Setups, and Trade with Confidence Using the Most Effective Candlestick Patterns and Chart Strategies](https://cdn.blogweb.me/1/51_Jozc_NDI_6_L_SL_160_789bb784f0.jpg)
The Candlestick Trading Bible [50 in 1]: Learn How to Read Price Action, Spot Profitable Setups, and Trade with Confidence Using the Most Effective Candlestick Patterns and Chart Strategies
![The Candlestick Trading Bible [50 in 1]: Learn How to Read Price Action, Spot Profitable Setups, and Trade with Confidence Using the Most Effective Candlestick Patterns and Chart Strategies](https://cdn.flashpost.app/flashpost-banner/brands/amazon.png)
![The Candlestick Trading Bible [50 in 1]: Learn How to Read Price Action, Spot Profitable Setups, and Trade with Confidence Using the Most Effective Candlestick Patterns and Chart Strategies](https://cdn.flashpost.app/flashpost-banner/brands/amazon_dark.png)
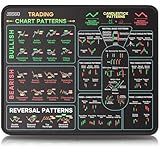
JIKIOU Stock Market Invest Day Trader Trading Mouse Pad Chart Patterns Cheat Sheet, Standard Computer Mouse Pad/Desk Mat with Stitched Edges Black 10.2x8.3 inch
- UNIQUE DESIGN: INSPIRING LUCK AND SUCCESS IN STOCK MARKET INVESTING.
- COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS: QUICK-REFERENCE CHARTS FOR EASY TRADING DECISIONS.
- DURABLE & PRACTICAL: NON-SLIP BASE AND LASTING QUALITY FOR DAILY USE.



My Trading Journal - Premium Log Book for Stock Market, Forex, Options, Crypto - Guided Trading Journal with 80 Trades, 8 Review Sections - Ideal for Day Traders, Swing Traders, Position Traders
-
TRACK AND ANALYZE TRADES TO BOOST YOUR TRADING PERFORMANCE SECURELY.
-
RECORD 80 GUIDED TRADES TO REFINE STRATEGIES AND MAXIMIZE PROFITS.
-
VERSATILE FOR STOCKS, FOREX, AND CRYPTO-SUPPORTING ALL TRADING STYLES!



How to Day Trade for a Living: A Beginner’s Guide to Trading Tools and Tactics, Money Management, Discipline and Trading Psychology (Stock Market Trading and Investing)
- WORK FROM ANYWHERE: FREEDOM TO TRADE ON YOUR TERMS.
- BE YOUR OWN BOSS: ANSWER ONLY TO YOURSELF FOR ULTIMATE CONTROL.
- SUCCESS REQUIRES TOOLS, MOTIVATION, AND PERSEVERANCE.


Support and resistance levels are key concepts in technical analysis that help traders identify potential entry and exit points for their trades. In this tutorial, we will be using the programming language Julia to calculate and plot support and resistance levels for a given stock or financial instrument.
To calculate support and resistance levels, we will first need historical price data for the stock or instrument we are interested in. Once we have this data, we can use mathematical algorithms and statistical methods to identify key levels where the price is likely to encounter obstacles. These levels can serve as important reference points for traders looking to make informed decisions about their trades.
In Julia, we can use libraries such as DataFrames and Plots to import and visualize the historical price data. We can then apply methods such as moving averages, trendlines, and pivot points to identify potential support and resistance levels. By plotting these levels on a chart along with the price data, we can visually see how they interact with the price movements over time.
Overall, understanding support and resistance levels can help traders make more informed decisions and improve their overall trading strategies. By using Julia to calculate and visualize these levels, traders can gain deeper insights into the dynamics of the market and potentially increase their chances of success.
How to conduct a correlation analysis between support and resistance levels and other indicators?
To conduct a correlation analysis between support and resistance levels and other indicators, follow these steps:
- Collect the data: Gather historical price data for the asset you are analyzing, including support and resistance levels and the other indicators you want to correlate with them.
- Calculate the correlation coefficient: Use a statistical software program or an online tool to calculate the correlation between support and resistance levels and the other indicators. The correlation coefficient ranges from -1 to 1, with 0 indicating no correlation, 1 indicating a perfect positive correlation, and -1 indicating a perfect negative correlation.
- Interpret the results: Analyze the correlation coefficient to determine the strength and direction of the relationship between support and resistance levels and the other indicators. A positive correlation suggests that the two variables move in the same direction, while a negative correlation indicates they move in opposite directions.
- Consider the significance: In addition to the correlation coefficient, also look at the p-value to determine if the correlation is statistically significant. A p-value below 0.05 is typically considered statistically significant.
- Use the results to inform your trading strategy: If you find a strong correlation between support and resistance levels and other indicators, you can use this information to make more informed trading decisions. For example, if a particular indicator consistently confirms support or resistance levels, you may use it as a signal to enter or exit a trade.
- Monitor and adjust: Continuously monitor the correlation between support and resistance levels and other indicators over time, and be prepared to adjust your trading strategy if the relationship changes. Remember that correlation does not imply causation, so always conduct further analysis and consider other factors before making trading decisions.
What is the role of support and resistance in technical analysis?
Support and resistance levels are key concepts in technical analysis that help traders and analysts identify potential price reversal points for an asset.
Support level is a price level where a downtrend can be expected to pause or reverse, as buying interest is expected to be strong enough to prevent the price from declining further. It acts as a floor for the price, preventing it from falling below that level.
Resistance level, on the other hand, is a price level where an uptrend can be expected to pause or reverse, as selling interest is expected to be strong enough to prevent the price from rising further. It acts as a ceiling for the price, preventing it from going higher.
Traders and analysts use support and resistance levels to make trading decisions, such as entering or exiting positions, setting stop-loss orders, or identifying potential price targets. These levels can also provide valuable insights into the strength of a trend, as well as potential levels for price reversals.
By understanding and analyzing support and resistance levels, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their chances of successful trading.
What are some common indicators used to determine support and resistance levels?
- Previous swing highs and lows: Traders often look to previous highs and lows in price as potential support and resistance levels.
- Moving averages: Moving averages, such as the 50-day or 200-day moving average, can act as dynamic support and resistance levels.
- Fibonacci retracement levels: Traders use Fibonacci ratios, such as the 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% levels, as potential support and resistance levels.
- Psychological levels: Round numbers, such as $50 or $100, are often seen as psychological support and resistance levels.
- Pivot points: Pivot points are calculated based on previous price levels and are used to identify potential support and resistance levels.
- Trendlines: Trendlines, drawn by connecting swing highs or lows, can act as support or resistance levels depending on the direction of the trend.
- Volume profile: Volume profile analysis can help identify areas of high trading activity, which can act as support or resistance levels.
